Non-Invasive prenatal testing (NIPT)
We are introducing the NIFTY/NIPT (Non-Invasive Fetal Trisomy Test), the first NIPT Test available worldwide from 2010 and with clinical validation by a study of over 147,000 pregnancy cases. Since then as of August 2022, over 11.5 million NIFTY tests have been performed globally.
| NIFTY- Basic includes |
| Trisomy includes |
| Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) |
| Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) |
| Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome) |
| Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies |
| XXY (Klinefelter Syndrome) |
| Monosomy X (Turner Syndrome) |
| XXX (Triple X) |
| XYY (Jacobs Syndrome) |
| Sex Indication |
| Y chromosome detection |
NIFTY pro – includes |
Trisomy of all autosomes, including |
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) |
Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) |
Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome) |
| Trisomy 22 |
| Trisomy 16 |
| Trisomy 9 |
Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies |
XXY (Klinefelter Syndrome) |
Monosomy X (Turner Syndrome) |
| XXX (Triple X) |
XYY (Jacobs Syndrome) |
| Sex Indication |
Y chromosome detection |
84 micro deletion/ duplication, including: |
5p (Cri-du-Chat syndrome) |
| 1p36 |
| 2q33.1 |
DiGeorge Syndrome (22q11.2) |
| 16p12 |
Jacobsen Syndrome(11q23) |
Van der Woude Syndrome (1q32.2) |
Prader-Willi / Angelman Syndrome (15q11.2) |
What is NIPT
NIPT is a blood test that is more accurate than the first pregnancy screening test. It’s offered to women who are carrying a baby identified from previous screening tests as having a higher chance of having either Down’s syndrome, Edwards’ syndrome, or Patau’s syndrome.
NIPT offers screening for some of the most common trisomies present at birth, including trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome) and trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome). NIFTY also provides testing options for sex chromosomal aneuploidies, chromosomal deletions/duplications, and gender.
- Suitable for: Pregnant women from week 10 of pregnancy
- Turnaround time for the tests: under 7 working days
- Sample: Painless and risk-free Mother’s Venous blood sample (whole blood)
- Quantity: 10 ml Mother blood
- Technology: Whole genome sequencing (DNA sequencing)
- It has a sensitivity- of above 99% for trisomy disorders such as Down, Edwards, and Patau syndromes.
- It is a safe procedure- that simply requires a blood sample from the mother – there is no risk of miscarriage.
- Of course- it is quick-findings are delivered in less than 7 working days.
- And Yes-it is for pregnant women starting at week 10 of their pregnancy.
Is NIPT safe?
NIPT is completely safe for both you and your baby.
Why Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing?
Many prenatal screening options already exist. However , compared our NIFTY non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) other traditional screening methods suffer from lower accuracy and higher false positive rates.
When you finds the genetic abnormaity in the screening test then you can choose Invasive diagnostic tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are accurate but carry a 1-2% risk of miscarriage.
Should I have NIPT?
The NIPT test offers you primary screening test before you needs to have an intensive and invasive test which takes time, requires hospital environment and risk to baby associated with the procedure .
NIPT It can also help you prepare for the arrival of a baby who may need additional care and support.
The NIFTY test is SUITABLE for, but not limited to, patient who exhibit any of the following indications: |
Maternal age 35 years or older at delivery
|
Contraindications for invasive prenatal testing, such as placenta prevaria, risk of miscarriage, HBV infection etc. |
History of a prior pregnancy with a chromosomal abnormality |
Fetal ultrasonographic findings indicating an increased risk of T21, T18 or T13 |
Requires reassurance following previous screening result |
Received IVF treatment or has previously suffered from habitual abortion |
The NIFTY test is NOT SUITABLE for patient with the following indications: |
Maternal, fetal and/or placental mosaicism (mixtures of chromosomally normal and abnormal cells in the pregnancy) |
Mother or Father have chromosomal abnormality (translocation or inversion) |
Patients who have received a blood transfusion within one year prior to testing date |
Patient who have had transplant surgery |
Patients who have had stem cell therapy |
Vanishing twin syndrome (with developmental arrest identified as having occurred after week 8 of pregnancy and/or within 8 weeks of NIFTY® testing) |
How accurate is NIPT?
Based on a study of over 147,000 pregnancies, it has demonstrated >99% sensitivity for T21, 18, and 13.
Test Methodology
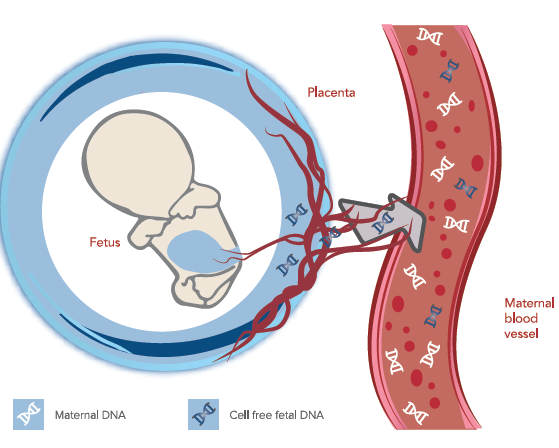
During pregnancy, Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) fragments originating from both the mother and fetus (cffDNA) are present in maternal blood circulation.
The NIFTY test requires a small amount of maternal blood, and the test goes through a detailed Genomic abnormality test from the fetus DNA extracted from the mother’s blood sample to detect chromosomal abnormalities. Small excesses or deficits in counts of the affected chromosome will be detected if aneuploidy is present.
The Test Workflow
- For further information about the test, call 03001246500 or email enquiry@hasudiagnostics.com
- Our Team will explain about the test.
- When you arrive at the clinic on the appointment day, our well-trained phlebotomist will draw the venous blood.
- Tests take five working days after the sample received by our partner lab.
- Our expert will analyse and send you the test report and support if requires any further clarification over the phone.
Trisomies
A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy in which there are three chromosomes instead of the usual pair. Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) and Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) are the three most commonly occurring autosomal chromosome aneuploidies in live births. These chromosomal conditions are caused by the presence of an extra copy or partial copy of chromosome 21, 18 or 13 respectively. This additional genetic material can cause dysmorphic features, congenital malformation, and different degrees of intellectual disability.
Deletion Syndromes
Deletion syndromes are defined as a group of clinically recognizable disorders characterized by a small deletion of a chromosomal segment. The size and position of the deletion determine which clinical features are manifested and how severe they are.
Clinical features of deletions can include developmental delays and intellectual disability, and growth.
differences, behavioral problems, feeding difficulties, low muscle tone, seizures, dysmorphic features, and a pattern of varying malformations.
Sex Chromosomal Aneuploidies
Sex chromosome aneuploidy is defined as a numeric abnormality of an X or Y chromosome, with addition or loss of an entire X or Y chromosome. Although most cases of sex chromosome aneuploidies are generally mild without intellectual disability, some have a well-established phenotype that can include physical abnormalities, learning delays and infertility.










